


Nigeria's Stocks Fall to Three-Year Low as Foreigners Exit
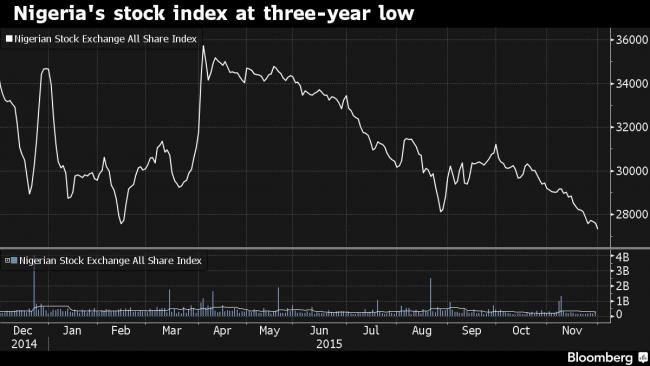
Nigeria’s stocks fell to their lowest level in almost three years as foreigners exited the market amid fading hopes that President Muhammadu Buhari’s government can revive an economy growing at its slowest pace this century.
The Nigerian Stock Exchange All Share Index dropped 0.8 percent to 27,385.69 at close in the commercial capital of Lagos, the lowest since December 2012. The gauge declined on all but three trading days in November for a monthly drop of 6.2 percent.
“The government has not come up with a definitive policy for the economy,” Pabina Yinkere, an analyst at Vetiva Capital Management Ltd., said by phone from Lagos. “The continued lack of clarity is affecting the stock market.”
While Buhari, a 72-year-old former general who came to power in May, has prioritized stamping out corruption in Africa’s biggest economy and oil producer, investors were irked by a delay of more than five months in forming a cabinet, which he swore in Nov. 11. There’s also concern that his support for the central bank’s currency-trading restrictions are choking businesses of the dollars they need to pay foreign suppliers.
Almost two stocks declined for every one that rose. Guaranty Trust Bank Plc, the nation’s biggest lender by market capitalization, dropped 2.7 percent to 20 naira ($0.10). The stock is down 21 percent this year, about the same as the overall index. That’s the biggest fall in sub-Saharan Africa after the Zimbabwe Industrial Index.
Specialist African funds including Alquity Investment Management Ltd. and Duet Asset Management Ltd. have lowered their Nigerian exposure because they think that central bank Governor Godwin Emefiele will be forced to devalue the naira, which would cause losses on holdings in foreign-currency terms. Last week’s interest rate cut by the central bank, its first in six years, will heap more pressure on the currency, according to David McIlroy, Alquity’s chief investment officer.
The naira was unchanged at 199.05 per dollar and has been all but fixed at 198 to 199 since early March. Forward prices suggest it will weaken to 241.25 in a year.
Pressure on Currency
“The surprise reduction in rates has probably worried international investors even more,” McIlroy said by phone from London. “Given the inflation rate is above the central bank’s target, there’s pressure on the currency and they need to attract foreign capital, you’d expect interest rates to be rising.”
Annual inflation was 9.3 percent in October, higher than the central bank’s target of 6 percent to 9 percent.
Alquity held about seven Nigerian stocks at the beginning of 2015, including Guaranty Trust Bank and Zenith Bank Plc. It now holds only Dangote Cement Plc. Equity funds are more underweight in Nigeria than any other frontier and emerging market, except for Kuwait and Morocco, analysts at Renaissance Capital Ltd. said in a Nov. 23 note to clients.
“We’ve increased our positions in Egypt and Kenya at the expense of Nigeria,” McIlroy said.
Nigeria is reeling from crude prices that have plunged 57 percent since June 2014. Economic growth will slow to 3.2 percent this year from 6.3 percent in 2014, according to a Bloomberg survey of economists. That would be the slowest pace since 1999.
Source: BloombergBusiness
Share this post
Naijanetwork Forum Statistics
Threads: 14869,
Posts: 17928,
Members: 6717


